Patellofemoral pain syndrome (commonly called runner's knee) describes pain in the patellofemoral joint (kneecap and front part of femur) that is caused by overuse rather than by a traumatic injury. Other names for patellofemoral pain syndrome include "chondromalacia patellae" (a reference to the degeneration of cartilage in the joint) and "moviegoer’s knee" (since some people feel pain during periods of prolonged sitting).
Although this pain may first become apparent during athletic activities such as running, it is also evident with everyday activities. Patients often notice it when:
- Going up – and especially downstairs
- After sitting for a long time, with the transition from sitting to standing
- When squatting, kneeling and lunging
- Wearing high heels can also exacerbate symptoms
The pain is usually less pronounced when walking on level ground.
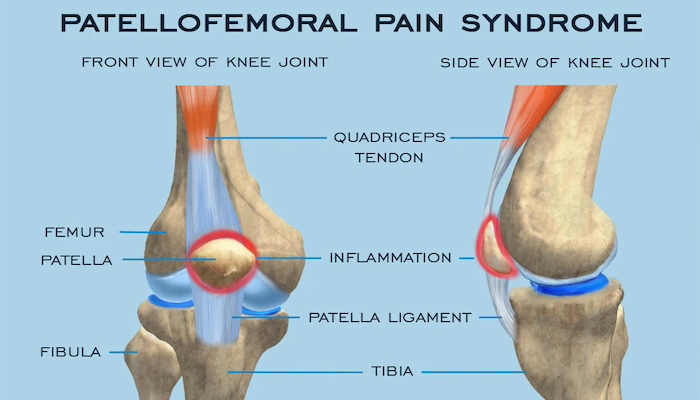
Anatomy of Runner's Knee
The pain is often found at the lower and outer areas of the kneecap – underneath the patella and at the outside of the knee. However, patients may also experience pain over the whole joint, or in severe cases, in the back of the knee.
Patients with this syndrome have an uneven distribution of stress or load underneath the kneecap that is causing pain. Sometimes, this is due to an abnormal tilt of the patella which can be seen on X-ray but it can also be seen in the setting of normal X-rays secondary to weakness in the large muscle groups of the leg. It’s as if the joint is like a seesaw that has too many children on one side. That extra stress on that side of the seesaw is similar to what one area of the knee is subject to every time you bend and straighten the joint.
Because patellofemoral pain inhibits the quadriceps muscle (the major muscle in front of the thigh) from doing its “job” of unloading stress on the kneecap, once pain occurs, it often progresses.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome – as well as other problems with the patella – are seen far more frequently in women than in men. Women naturally stand in a more valgus or knock-kneed position, a posture that automatically pulls the patella toward the outside of the leg and places the knee at risk for this uneven stress distribution.
Overly tight muscles and soft tissues that support the knee, including the hamstring muscles and the iliotibial (IT) band (the connective tissue that runs down the outer side of the thigh to the patella), can also lead to the condition. Conversely, women with hypermobile, loose soft tissues can also develop the syndrome owing to weakness and the failure of supporting muscles to balance or unload the patella, thereby allowing it to be pulled laterally away from the trochlea.
Orthopedists evaluate patellofemoral pain with a thorough physical exam which includes the assessment of any imbalances that may be present from the feet up. In addition to a tilted patella, pain can be exacerbated by other factors that place extra stress on the bone including flat feet, abnormal rotation of the hips, tightness of the IT band, and hip flexors. MRI and X-ray images may also be obtained.
Treatment for Patellofemoral Pain
The majority of people with patellofemoral pain syndrome can be treated non-operatively. The first goal of treatment is to “quiet the knee” with anti-inflammatory medications, application of ice, and relative rest. Patients must also alter any activities that are exacerbating the condition, avoiding participation in impact sports, high-intensity workouts, squats, or lunges, and minimizing stair climbing, at least temporarily.
In cases where an anatomical issue such as flat feet plays a role, orthotics may be prescribed. In patients who run, if irregularities in landing – such as pronation or supination – are contributing to the pain, a different shoe may be required. In some cases, a cortisone injection may be helpful to decrease inflammation in the knee so that the patient can tolerate a stretching and strengthening program.
A physical therapy regime is initiated to loosen tight tissues if present, and to improve structural strength throughout the leg and hip. In some cases, when physical therapy doesn’t yield the expected improvement further imaging is obtained such as MRI with specialized sequences to detect early cartilage changes. Occasionally a running analysis is performed at the Hospital for Special Surgery, as it may reveal an underlying gait abnormality that needs to be addressed.
Some patients seek care for patellofemoral pain syndrome because of persistent pain after undergoing a surgery called a lateral release or a chondroplasty or “clean-up”. These are fairly simple procedures in which the surgeon uses a small camera and instruments to release the lateral retinaculum or smooth out areas of arthritis. Continuing pain indicates that other factors contributing to the syndrome have not been addressed, often “cleaning up” areas of worn cartilage does not help patellofemoral pain.
The lateral release can be helpful in conjunction with a larger surgery such as a tibial tubercle osteotomy or a medial patellofemoral ligament (MPLF) reconstruction as part of the overall soft tissue balancing, but this procedure is rarely effective in isolation. These include individuals who have a tilted patella and intact cartilage, and who have not responded to extensive physical therapy. This is the overwhelming minority of patients with the syndrome, more than 95% of these patients do not require surgery.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens, and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Queens office at (718) 215-1888 or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialist, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko.